Clean air is an essential component of our environment. It is constantly being polluted due to various reasons, which poses a risk to both animals and humans. One of the main causes of Air Pollution is Particulate matter (PM). In this blog post, we will explore the invisible threats present in the air, including fine particles like PM2.5 and PM10, and their associated health risks. We will also discuss how air purifiers can help purify this pollution, allowing us to breathe clean and pure air. Air purifiers, the Smart Home Appliances can act as a frontline defense against air pollution and help create a healthier world with safer air. Through this article, we aim to educate readers on the importance of clean air and how air purifiers can play a crucial role in achieving it.
What is Particulate Matter
Particulate Matter (PM) refers to tiny particles or droplets in the air that can be composed of various substances, including solids and liquid droplets. These particles vary in size and can be classified into different categories based on their diameter. The two common classifications are:
PM2.5 (Particulate Matter with a diameter of 2.5 micrometers or smaller):
These are fine particles that are smaller than 2.5 micrometers in diameter. They can penetrate deep into the respiratory system, reaching the lungs and even entering the bloodstream. Sources of PM2.5 include combustion processes, vehicle emissions, industrial activities, and natural sources like wildfires.
PM10 (Particulate Matter with a diameter of 10 micrometers or smaller):
These particles are larger than PM2.5 but still small enough to be inhalable. PM10 can irritate the eyes, nose, and throat and can also reach the respiratory system. Sources of PM10 include construction activities, unpaved roads, agricultural operations, and industrial processes.
Health Impact:

PM2.5 and PM10 can have adverse effects on human health.
-
- Respiratory System: These particles can penetrate the respiratory system, leading to respiratory issues.
-
- Cardiovascular Issues: In addition to respiratory problems, exposure to PM is linked to cardiovascular problems.
World Health Organization (WHO) Guidelines: Safe Level Defination
- The WHO has established guidelines to monitor and maintain air quality.
- For PM2.5: The annual mean level should be kept below 10 µg/m³ to be considered safe.This means that, on average, the concentration of PM2.5 in the air over the course of a year should not exceed 10 micrograms per cubic meter.
-
Top 8 Cities with Highest Annual Average PM2.5 (µg/m³) in 2023: 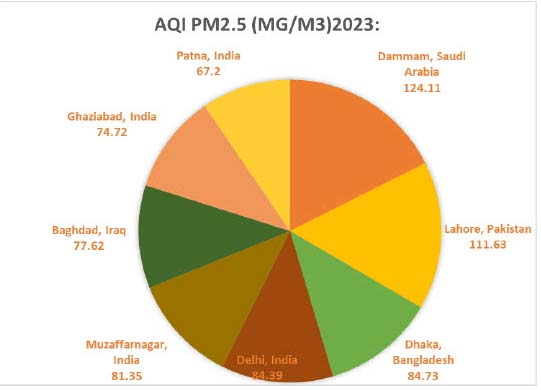 For PM10: The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends an annual mean level below 15 µg/m³ for safe air quality. This means that, on average, the concentration of PM10 particles in the air over the course of a year should not exceed 15 micrograms per cubic meter.
For PM10: The World Health Organization (WHO) recommends an annual mean level below 15 µg/m³ for safe air quality. This means that, on average, the concentration of PM10 particles in the air over the course of a year should not exceed 15 micrograms per cubic meter.-
Top 8 Cities with Highest Annual Average PM10(µg/m³) in 2023: 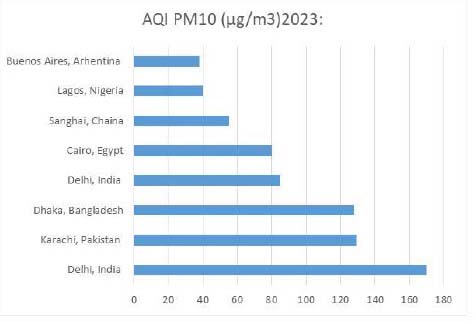
- Monitoring and Regulation:
Governments and environmental agencies use monitoring stations to measure PM levels in the air.
-
- Regulations and policies are implemented to control sources of PM, such as industrial emissions and vehicular pollution.
-
- Individuals are advised to take precautions, especially in areas with high PM concentrations.
-
- Wearing masks, staying indoors during high pollution periods, and using air purifiers can help reduce personal exposure.
Global Impact:
-
- PM is a global concern, and international efforts are made to address air quality issues.
-
- Cross-border cooperation is essential to tackle sources of PM that can travel long distances.
Public Awareness:
-
-
- Public awareness campaigns educate people about the health risks associated with PM exposure.These campaigns encourage behavioral changes to minimize individual contributions to air pollution.
-
Research and Innovation:
-
-
- Ongoing research explores innovative solutions to mitigate PM pollution.Technologies for cleaner energy, emission controls, and sustainable urban planning contribute to reducing PM levels.
-
It’s essential to stay informed about PM levels in your environment and actively participate in efforts to improve air quality for the well-being of individuals and communities.
How Air purifiers Tackle Air Pollution: Particulate Matter (PM):

Your Smart Home Appliances Air purifiers work to improve air quality and reduce air pollution by employing various technologies designed to capture and eliminate pollutants. Here’s how air purifiers help fix air pollution:
1. Filtration Systems:

- HEPA Filters: High-efficiency particulate Air (HEPA) filters are effective at capturing particles, including dust, pollen, pet dander, and PM2.5 and PM10.
- Activated Carbon Filters: These filters adsorb gases and odors, including volatile organic compounds (VOCs) and Pre-Filters: Capture larger particles, extending the lifespan of HEPA filters.
2. Particle Removal:
- Air purifiers can efficiently remove airborne particles, preventing them from being inhaled and reducing respiratory and cardiovascular health risks.
3. VOC Removal:
- Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) released from household products, paints, and cleaning agents are targeted and reduced, improving indoor air quality.
4. Ozone Conversion:
- Some air purifiers use ozone generators to convert harmful gases into harmless substances, enhancing the overall air quality.
5. UV-C Light Technology:
- Ultraviolet (UV) light can be used to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms, contributing to a healthier indoor environment.
6. Ionization:
- Air purifiers with ionizers release charged ions that attract and neutralize particles, causing them to fall out of the air.
7. Smart Air Quality Monitoring:

- Many modern air purifiers come with sensors to monitor air quality. They adjust their operation based on real-time pollution levels, ensuring optimal performance.
8. Reducing Allergens:
- By capturing and eliminating allergens like pet dander, mold spores, and pollen, air purifiers create a healthier living space for individuals with allergies or respiratory conditions.
9. Smoke and Odor Removal:
- Activated carbon filters effectively capture and neutralize smoke particles and odors, improving the overall air freshness.
10. Circulation and Ventilation:
- Air purifiers enhance air circulation and ventilation in enclosed spaces, preventing the buildup of pollutants.
11. Filter Replacement and Maintenance:
- Regular maintenance, including filter replacement, ensures the continued effectiveness of the air purifier in capturing pollutants
While air purifiers are effective in indoor environments, it’s important to note that they may not address outdoor air pollution sources. Therefore, a comprehensive approach to reducing air pollution includes outdoor pollution control measures, such as emission regulations, green spaces, and sustainable urban planning. Additionally, combining air purifiers with good ventilation practices and minimizing pollution sources indoors contributes to a healthier living environment. Smart Home Appliances, including advanced air purifiers, play a crucial role in creating cleaner and safer indoor air quality, employing innovative technologies to combat particulate matter (PM) and other pollutants.

Leave a Reply